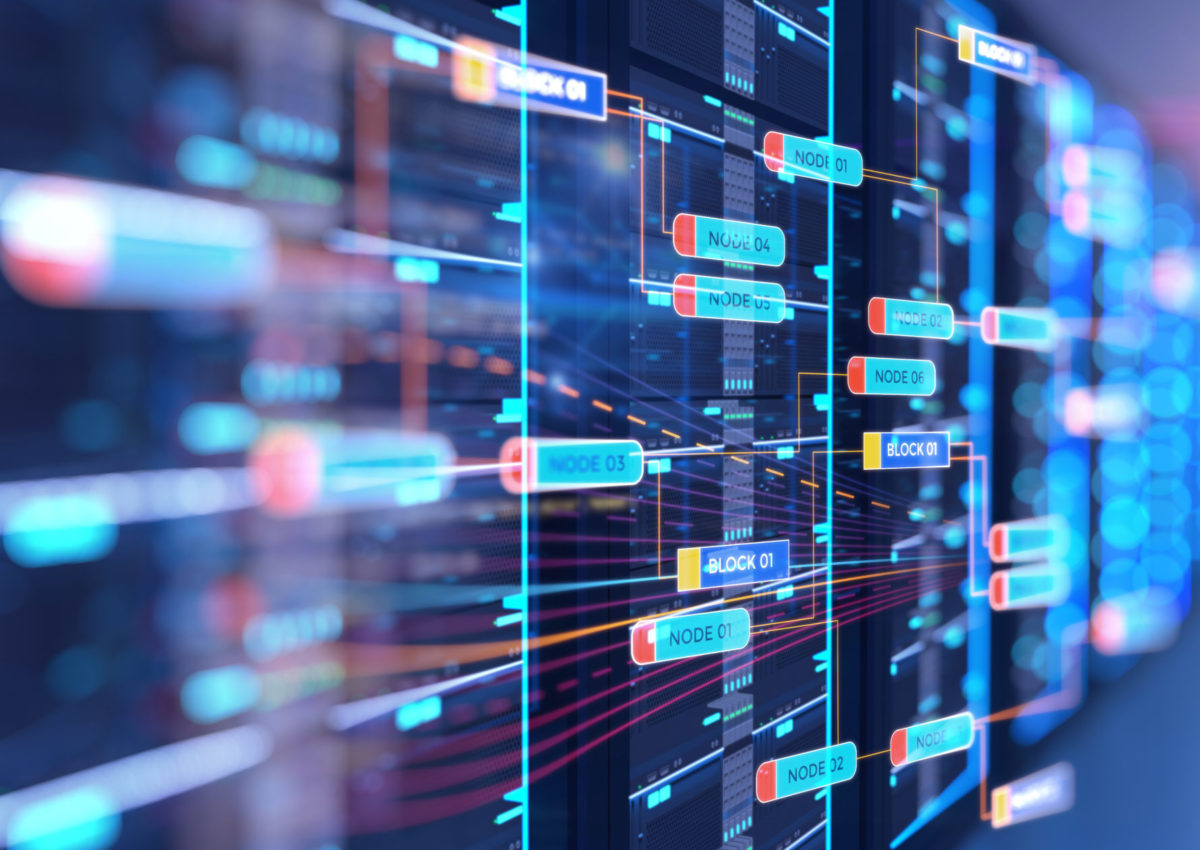
Leaving legacy applications alone, even when they become obsolete, is risky. In the long run, this limits technological growth and leaves companies open to security risks.
Alternatively, it can be cost prohibitive to retrieve data from these old systems. However, this data is often essential for legal or operational reasons.
Data Storage
Keeping legacy data in old systems that aren’t compatible with new technologies can hinder growth. New digital technology systems can offer a variety of advantages, including increased efficiency and lower costs. However, a company with an outdated database system can’t benefit from these advancements if the information isn’t accessible.
This is because new systems are usually designed for mobile devices and cloud platforms, while the legacy data can’t be easily transferred to the new system. Trying to make older systems work with new technologies is costly, time-consuming, and leaves the company vulnerable to security risks.
To mitigate this problem, the organization should develop a data migration strategy to convert legacy files into a format that can be easily used by newer systems. This should include a plan to secure the legacy data against unauthorized access, including data encryption and additional firewalls. In addition, a plan should be established to monitor the integrity of the data and take corrective measures when necessary.
Data Security
Legacy systems may not be compatible with newer hardware and software, which can lead to security risks. Organizations might have to invest in specialized tools and services to manage these systems effectively. They also might need to work with legacy data migration tools to ensure that the legacy data can be read and converted into a format that the new system can use.
It would be tempting to simply throw out the old system and all the information that’s stored in it, especially if it’s no longer useful or can’t be easily accessed by new technologies. However, this would be a short-term solution that could result in loss of valuable data. The best long-term strategy is to make sure the legacy information can be retrieved and transferred securely to a modern database. Then, the new technology can be integrated with the old to improve efficiency and save time. This is a critical component of high-quality data management.
Data Access
New digital technologies are often incompatible with legacy systems, and they can thwart productivity and growth. Whether it’s an inability to scale, support a growing user base, maintain speed, or deliver data in real time, these limitations make an organization slow and plodding, rather than fast and effective.
Another concern is that if the legacy system were to break or die, it could render critical data inaccessible. Losing that information would be devastating for many service-based enterprises.
The best way to address this issue is to encapsulate the access to the legacy database within a class that your application can call. This reduces coupling with a specific database and allows your applications to remain flexible and nimble as they grow with your business. It’s also a great idea to use the migration process as an opportunity to clean up your legacy data, eliminating duplicate records, incomplete rows, and improperly formatted entries. This will also help you prepare the data for its new home and ensure that it fits well in your new architecture.
Data Migration
Typically, data migration involves the transfer of legacy information to newer software environments. It can also involve data conversion or data integration, depending on the business case.
For example, a company may have historical records on obsolete systems that need to be migrated for archive purposes or in the event that hardware breaks down and renders the system unusable. Alternatively, an outdated database environment limits growth and might not support new data management tools and systems, which can limit a company’s ability to reach its objectives.
Migrating to a modern database environment can improve performance and scalability, and offer new capabilities the old system cannot provide. It can also improve decision-making by enabling insights based on real data and reducing siloed information. Ultimately, data migration can be a very complex process that requires a combination of science and art. Be sure to document the process thoroughly and create a comprehensive test plan. This will help you ensure that the new database is populated with high-quality data and doesn’t suffer from issues like duplicates or inaccurate information.